FHD vs HD: Breaking Down the Resolution Debate
The discussion between FHD & HD resolutions has become a key topic for anyone planning to upgrade their display technology. As digital technology evolves, the role of resolution in delivering exceptional visual experiences is more important than ever. With FHD offering four times the pixel count of HD, it’s clear that resolution significantly impacts image quality on our screens. This article dives into the differences between these two resolutions to help you decide which is the right choice for your needs.
Key Features of FHD & HD
1. FHD (Full High Definition)
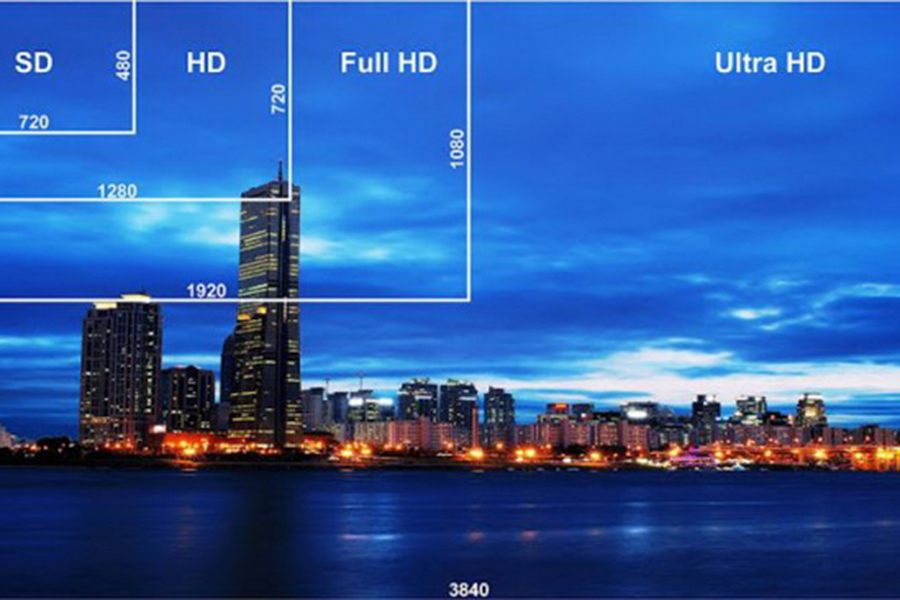
FHD, also known as Full High Definition, has become the gold standard for high-quality screens. It usually refers to a resolution of 1920×1080 pixels, which is four times sharper than standard HD. This means that FHD displays more pixels in the same screen area, resulting in clearer, more detailed images.
Definition & Standards: FHD is defined by 1920 pixels horizontally & 1080 vertically. It’s also called 1080p, with the “p” standing for progressive scan, where every line in the frame is drawn in one go. This method creates a smoother image, especially in fast-moving scenes.
Pixel Density: Pixel density, measured in pixels per inch (PPI), plays a vital role in display sharpness. A higher PPI means more pixels per inch, leading to clearer images. FHD screens generally have a higher PPI than HD, allowing for better detail & crisper text.
Applications: FHD is ideal for tasks requiring superior image quality. Gamers benefit from its sharp graphics & smooth motion. Video editors rely on FHD’s clarity for precise edits & color corrections. For streaming, FHD ensures crisp visuals, even on bigger screens.
2. HD (High Definition)
HD, or High Definition, has been around for some time & is often associated with a 1280×720 pixel resolution. While it doesn’t match FHD in detail, HD remains a popular choice due to its balance of quality & cost-effectiveness.
Definition & Standards: HD is defined by a resolution of 1280×720 pixels, also known as 720p. The “p” here also stands for progressive scan, ensuring a smooth image display. Although HD has a lower pixel density than FHD, it still offers a noticeable upgrade from older SD resolutions.
Pixel Density: HD’s pixel density is lower than FHD’s, meaning images may seem less sharp, particularly on larger screens. However, on smaller screens or when viewed from a greater distance, this difference is less noticeable.
Applications: HD works well for most everyday tasks. Many standard streaming services offer content in HD, which is more than sufficient for most users. Casual gamers might not see a significant difference between HD & FHD, & for regular computing tasks, HD provides a good balance between quality & performance.
FHD vs HD Functions
1. Image Quality
FHD & HD displays differ greatly in terms of image quality. FHD offers more detailed, crisper visuals, while HD may appear softer, especially on larger screens or from up close. However, for many users, this difference may not matter much, as HD still offers a satisfying viewing experience.
2. Cost & Value
FHD displays & devices tend to cost more than HD alternatives. Whether the investment is worth it depends on what the user needs. Professionals or gamers who require high-quality visuals will find FHD worthwhile. On the other hand, casual users might prefer the cost savings of an HD device.
3. Device Compatibility
Not every device supports FHD resolution. When choosing a display, it’s essential to ensure compatibility with your devices & platforms. Some older models may not fully support FHD, making HD a more practical choice in such cases.
4. Content Availability
While FHD content is becoming more common, HD remains the standard for many streaming platforms & broadcast media. The decision between FHD & HD may depend on what type of content you consume most often.
FHD vs HD Resolution Comparison
| Parameter | FHD (1920 x 1080) | HD (1280 x 720) |
|---|---|---|
| Resolution | 1920 x 1080 | 1280 x 720 |
| Pixel Count | 2.07 Million Pixels | 0.92 Million Pixels |
| Aspect Ratio | 16:9 | 16:9 |
| Image Clarity | Sharper and more detailed than HD | Less sharp, lower pixel density |
| Common Use Cases | Television, Gaming, Media Streaming | Budget Displays, Projectors, Older TV Models |
| Screen Size Compatibility | Suitable for larger screens (40″-65″) | Typically used for smaller screens (24″-40″) |
| Pixel Density | Higher pixel density, resulting in crisper text and images | Lower pixel density, may appear pixelated on larger screens |
| Energy Consumption | Higher power consumption due to higher resolution | Lower power consumption |
| Price Range | Typically higher due to better resolution | More affordable, budget-friendly |
Conclusion
1. The Resolution Revolution
Resolution has been a key factor in display tech improvements. Looking ahead, resolutions like 4K & 8K are set to become more common, pushing visual experiences even further.
2. Choosing the Right Resolution
When deciding between FHD & HD, think about your needs, budget, & the type of content you enjoy. For most people, HD gives a good balance of quality & cost. But if you need top-tier visuals, FHD is the better choice.
3. The Future of Resolutions
The future of resolutions looks promising, with tech progress bringing more detailed & immersive visuals. As devices & content improve, our expectations for display quality will continue to rise.
4. Final Thoughts
In the end, choosing between FHD & HD is up to you, based on your needs & preferences. Keep up with the latest display tech to make the best decision for your viewing. Whether you go for the sharpness of FHD or the savings of HD, what matters most is that your display fits your digital life the best.